はじめに
はじめに
IoTや環境モニタリングにおいて、「温度」と「湿度」の計測は最も基本的ながら重要な機能です。低コストで手軽に使える DHT11 センサーと、手頃な開発ボード Raspberry Pi Pico を組み合わせれば、誰でも環境データを取得・表示するシステムを構築できます。
本記事では、DHT11 の特徴・接続・MicroPythonによる実装例さらには拡張・応用、注意点を含めて解説します。
DHT11とは?その仕様と特徴
基本仕様
- 測定温度範囲:0〜50 ℃(±2 ℃ 程度)
- 測定湿度範囲:20~90%RH(+/−5%RH 程度)
- 動作電圧:3.0〜5.5V 程度
- サンプリング周期:1回/秒程度(1 Hz)
- 出力方式:シングルワイヤ(データ線+プルアップ回路)でデジタル値を出力
特徴と限界
- 非常に低コストで、電子工作の入門用途に向いています。
- ただし、湿度・温度共に 高精度を必要とする計測用途には向いていません。たとえば、湿度については±5%程度の誤差が仕様上想定されています。
- 実際にユーザーフォーラム等では「DHT11 は湿度の読み値がずれることが多い」といった指摘もあります。
- そのため、精度を重視するならば上位機種(たとえば DHT22/AM2302 や BME280 等)を検討するのも有効です。
Raspberry Pi Picoに接続された温度と湿度センサー DHT11から情報を取得して表示します。
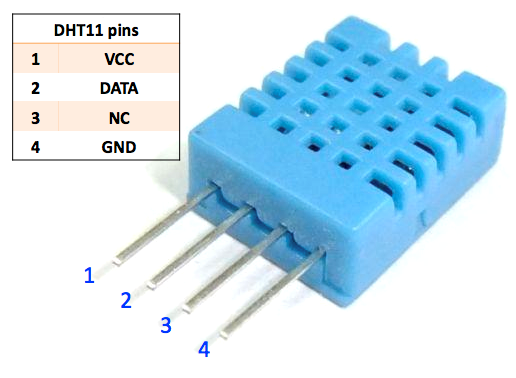
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/d2r2/go-dht/master/docs/DHT11.pdf
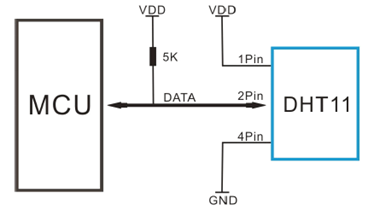
単一バスでは通常、バスがアイドル状態のときにそのステータスがハイレベルになるように、約 4.7 kΩ の外部プルアップ抵抗器が必要です。
Temperature and Humidity Sensor Module (DHT11) — SunFounder Universal Maker Sensor Kit documentation
MicroPython コード
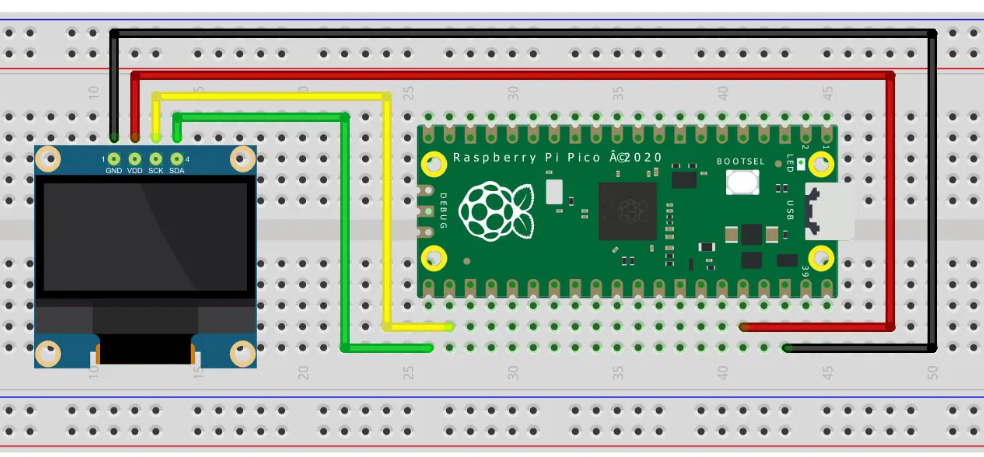
以下に、DHT11 を Pico に接続して温度・湿度を取得し、OLEDディスプレイ表示まで行うコード例を整理しました。
import dht # DHT センサー用ライブラリをインポート
from machine import Pin # GPIO 制御のために Pin クラスをインポート
import time # 遅延のために time モジュールをインポート
# DHT11 センサーを初期化
# DHT11 のデータピンを GPIO6 に接続(必要に応じて変更してください)
dht11 = dht.DHT11(Pin(6))
# 温度と湿度を継続的に読み取って表示
while True:
try:
# センサーに測定を指示
dht11.measure()
# センサーから温度を取得(摂氏)
temp = dht11.temperature()
# センサーから湿度を取得(パーセント)
hum = dht11.humidity()
# 測定結果をフォーマットして表示
print(f"温度: {temp:.1f}°C") # 例: "温度: 24.0°C"
print(f"湿度: {hum:.1f}%") # 例: "湿度: 60.0%"
except Exception as e:
# エラーが発生した場合(例: センサー未接続やチェックサムエラーなど)、エラー内容を表示
print("センサーの読み取りに失敗しました:", e)
# 次の測定まで 1 秒待機
time.sleep(1)
SSD1306 OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) display module
# Import required libraries
import dht # Library for DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor
from machine import Pin, I2C # Pin and I2C classes from machine module for GPIO and I2C communication
import time # For adding delays between sensor readings
import ssd1306 # SSD1306 OLED display driver library
# Initialize the DHT11 sensor
# The data pin of DHT11 is connected to GPIO6 (GP6 on Raspberry Pi Pico)
dht11 = dht.DHT11(Pin(6))
# Initialize the I2C interface and SSD1306 OLED display
# The display is connected using I2C with:
# - SCL (clock line) on GPIO17 (GP17)
# - SDA (data line) on GPIO16 (GP16)
# The screen resolution is 128x64 pixels
i2c = I2C(scl=Pin(17), sda=Pin(16))
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c)
try:
# Start an infinite loop to repeatedly read data from the sensor and display it
while True:
try:
# Measure temperature and humidity using the DHT11 sensor
dht11.measure()
temp = dht11.temperature() # Temperature in Celsius
hum = dht11.humidity() # Humidity in percentage
# Clear the OLED display before showing new data
oled.fill(0)
# Display temperature and humidity on the OLED screen
oled.text(f"Temp : {temp:.1f}*C", 0, 0) # Display temperature at top-left
oled.text(f"Humi : {hum:.1f} %", 0, 16) # Display humidity below it
# Send the buffer to the display
oled.show()
# Also print the values to the serial console for debugging/logging
print(f"Temperature: {temp:.1f}*C")
print(f"Humidity : {hum:.1f} %")
except Exception as e:
# If reading the sensor fails (e.g., connection issue or checksum error)
# Print the error to the console and show error on the OLED
print("Failed to read sensor:", e)
oled.fill(0)
oled.text("Sensor Error!", 0, 0)
oled.show()
# Wait for 1 second before taking the next reading
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# When script is manually stopped (e.g., Ctrl+C), clear the OLED
print("Script stopped by user. Clearing OLED display.")
oled.fill(0)
oled.show()SSD1306 OLED display driver
GitHub - stlehmann/micropython-ssd1306: A fork of the driver for SSD1306 displays to make it installable via upip
A fork of the driver for SSD1306 displays to make it installable via upip - stlehmann/micropython-ssd1306
# MicroPython SSD1306 OLED driver, I2C and SPI interfaces
from micropython import const
import framebuf
# register definitions
SET_CONTRAST = const(0x81)
SET_ENTIRE_ON = const(0xA4)
SET_NORM_INV = const(0xA6)
SET_DISP = const(0xAE)
SET_MEM_ADDR = const(0x20)
SET_COL_ADDR = const(0x21)
SET_PAGE_ADDR = const(0x22)
SET_DISP_START_LINE = const(0x40)
SET_SEG_REMAP = const(0xA0)
SET_MUX_RATIO = const(0xA8)
SET_IREF_SELECT = const(0xAD)
SET_COM_OUT_DIR = const(0xC0)
SET_DISP_OFFSET = const(0xD3)
SET_COM_PIN_CFG = const(0xDA)
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV = const(0xD5)
SET_PRECHARGE = const(0xD9)
SET_VCOM_DESEL = const(0xDB)
SET_CHARGE_PUMP = const(0x8D)
# Subclassing FrameBuffer provides support for graphics primitives
# http://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/pyboard/library/framebuf.html
class SSD1306(framebuf.FrameBuffer):
def __init__(self, width, height, external_vcc):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.external_vcc = external_vcc
self.pages = self.height // 8
self.buffer = bytearray(self.pages * self.width)
super().__init__(self.buffer, self.width, self.height, framebuf.MONO_VLSB)
self.init_display()
def init_display(self):
for cmd in (
SET_DISP, # display off
# address setting
SET_MEM_ADDR,
0x00, # horizontal
# resolution and layout
SET_DISP_START_LINE, # start at line 0
SET_SEG_REMAP | 0x01, # column addr 127 mapped to SEG0
SET_MUX_RATIO,
self.height - 1,
SET_COM_OUT_DIR | 0x08, # scan from COM[N] to COM0
SET_DISP_OFFSET,
0x00,
SET_COM_PIN_CFG,
0x02 if self.width > 2 * self.height else 0x12,
# timing and driving scheme
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV,
0x80,
SET_PRECHARGE,
0x22 if self.external_vcc else 0xF1,
SET_VCOM_DESEL,
0x30, # 0.83*Vcc
# display
SET_CONTRAST,
0xFF, # maximum
SET_ENTIRE_ON, # output follows RAM contents
SET_NORM_INV, # not inverted
SET_IREF_SELECT,
0x30, # enable internal IREF during display on
# charge pump
SET_CHARGE_PUMP,
0x10 if self.external_vcc else 0x14,
SET_DISP | 0x01, # display on
): # on
self.write_cmd(cmd)
self.fill(0)
self.show()
def poweroff(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP)
def poweron(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP | 0x01)
def contrast(self, contrast):
self.write_cmd(SET_CONTRAST)
self.write_cmd(contrast)
def invert(self, invert):
self.write_cmd(SET_NORM_INV | (invert & 1))
def rotate(self, rotate):
self.write_cmd(SET_COM_OUT_DIR | ((rotate & 1) << 3))
self.write_cmd(SET_SEG_REMAP | (rotate & 1))
def show(self):
x0 = 0
x1 = self.width - 1
if self.width != 128:
# narrow displays use centred columns
col_offset = (128 - self.width) // 2
x0 += col_offset
x1 += col_offset
self.write_cmd(SET_COL_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(x0)
self.write_cmd(x1)
self.write_cmd(SET_PAGE_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(0)
self.write_cmd(self.pages - 1)
self.write_data(self.buffer)
class SSD1306_I2C(SSD1306):
def __init__(self, width, height, i2c, addr=0x3C, external_vcc=False):
self.i2c = i2c
self.addr = addr
self.temp = bytearray(2)
self.write_list = [b"\x40", None] # Co=0, D/C#=1
super().__init__(width, height, external_vcc)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.temp[0] = 0x80 # Co=1, D/C#=0
self.temp[1] = cmd
self.i2c.writeto(self.addr, self.temp)
def write_data(self, buf):
self.write_list[1] = buf
self.i2c.writevto(self.addr, self.write_list)
class SSD1306_SPI(SSD1306):
def __init__(self, width, height, spi, dc, res, cs, external_vcc=False):
self.rate = 10 * 1024 * 1024
dc.init(dc.OUT, value=0)
res.init(res.OUT, value=0)
cs.init(cs.OUT, value=1)
self.spi = spi
self.dc = dc
self.res = res
self.cs = cs
import time
self.res(1)
time.sleep_ms(1)
self.res(0)
time.sleep_ms(10)
self.res(1)
super().__init__(width, height, external_vcc)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.spi.init(baudrate=self.rate, polarity=0, phase=0)
self.cs(1)
self.dc(0)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(bytearray([cmd]))
self.cs(1)
def write_data(self, buf):
self.spi.init(baudrate=self.rate, polarity=0, phase=0)
self.cs(1)
self.dc(1)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(buf)
self.cs(1)
__version__ = '0.1.0'
Lesson 19: Temperature and Humidity Sensor Module (DHT11) — SunFounder Universal Maker Sensor Kit documentation
Lesson 27: OLED Display Module (SSD1306) — SunFounder Universal Maker Sensor Kit documentation


コメント